Aenert news. Invention analysis
Hydrogen production via water electrolysis holds immense significance in modern world. As an alternative way of producing power, it offers a potential to address global challenges related to sustainability and climate change. It offers a diverse set of advantages for a society, including decarbonization of energy sector in cases where energy is produced from green sources, energy storage and grid balancing that is important for communities producing power from intermittent sources, greener transportation and industrial sector, and energy independence.
One of the major aspects in hydrogen production by water electrolysis is the efficiency of main process. It represents the performance of an electrolysis cell itself and its major components – cathode, anode, separator, and catalysts involved. It can include such important aspects as energy-efficiency of the process, start-up time, stability of the process, activity of catalysts and other elements that can ensure high reaction rate, etc.
Below is a short review of recent patents related to improvements in efficiency of main process with regard to hydrogen production via electrolysis of water. For the purpose of this review, we collected 2000 patents published in the past 5 years. The patents are considered applicable to the subject under consideration when they describe devices, methods, or compositions that can be used in or as electrolyzers and where authors indicate that their inventions are somehow aimed at improving the efficiency of processes occurring in the electrolyzers. In addition to that, the inventions may also concern other problems and other aspects of electrolysis.
Below is a list of the top applicants by their patenting share in the pool of recent patents on electrolysis aimed at solving the problems of low efficiency of main process.
Applicants’ share in the intellectual property market, %. Patents, 2019-2023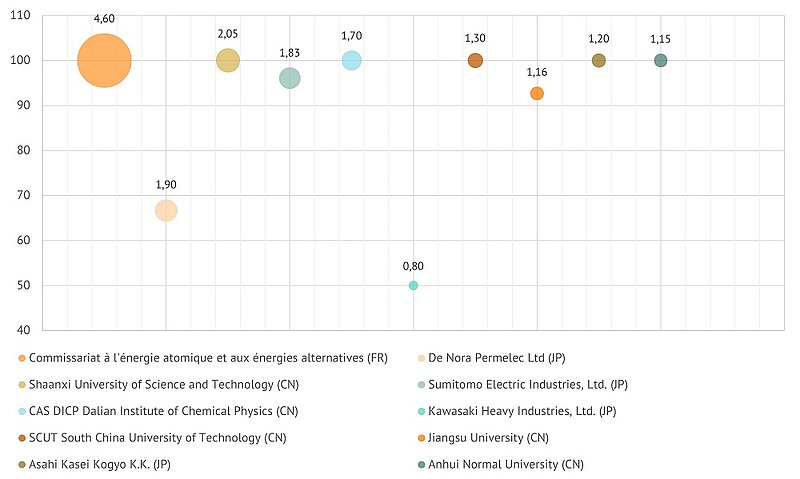
Value: Market involvement ratio*; Y axis: Ownership ratio; Bubble size: Volume ratio.
*(Market involvement ratio = volume ratio multiplied by ownership ratio, where Volume ratio - share of applicant documents in total number of documents, Ownership ratio - applicant's participation share in total number of documents)
Various types of electrolysis can be used to produce hydrogen from water. In this selection of documents, OEL, which includes documents where type of electrolysis was not clearly identified and documents attributed to other types of electrolysis, comprises almost a half of all patents. It is followed by Alkaline electrolysis, Polymer electrolyte membrane electrolysis, and Solid oxide electrolysis:
Recent patents by type of electrolysis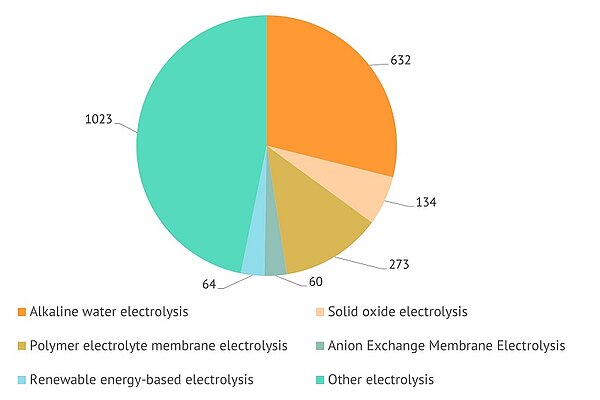
Another breakdown includes special aspects of electrolysis covered in the revised recent patents. Here, catalyst is clearly the most popular technological element. It is followed by inventions disclosing electrolyzer, anode, and cathode:
Recent patents by special aspects of electrolysis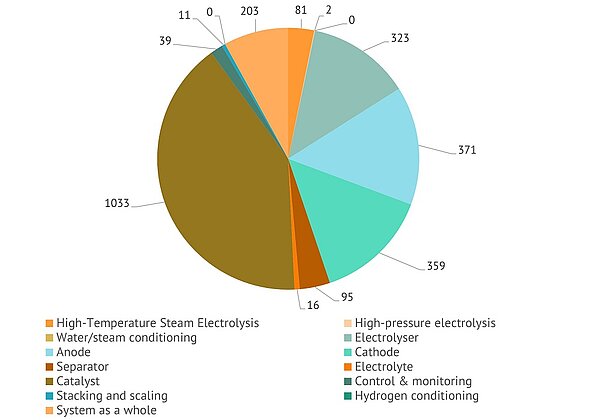
Below are top IPC indices that were assigned to the recent patents on low efficiency of main process in electrolysis of water:
| IPC | Share | IPCs assigned |
|---|---|---|
| C25B1/04 | 14% | 1403 |
| C25B11/091 | 4.9% | 492 |
| C25B11/06 | 2.1% | 210 |
| B82Y40/00 | 1.8% | 184 |
| C25B15/08 | 1.8% | 176 |
| C25B9/19 | 1.7% | 174 |
| B82Y30/00 | 1.6% | 159 |
| C25B9/23 | 1.5% | 154 |
| C25B11/031 | 1.5% | 150 |
| C25B11/075 | 1.5% | 150 |
According to the International Patent Classification, the IPC indices above have the following definitions: C25B1/04 - by electrolysis of water; C25B11/091 - consisting of at least one catalytic element and at least one catalytic compound; consisting of two or more catalytic elements or catalytic compounds; C25B11/06 - by the catalytic materials used; B82Y40/00 - Manufacture or treatment of nanostructures; C25B15/08 - Supplying or removing reactants or electrolytes; Regeneration of electrolytes; C25B9/19 - with diaphragms; B82Y30/00 - Nanotechnology for materials or surface science, e.g. nanocomposites; C25B9/23 - comprising ion-exchange membranes in or on which electrode material is embedded; C25B11/031 - Porous electrodes; C25B11/075 - consisting of a single catalytic element or catalytic compound.
In terms of rating points, following are the most prominent documents in the collection under consideration:
Rating: 21
CN114196966B / CAS DICP Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (CN) / Proton membrane and CCM (continuous current module) integrated preparation method and device for PEM (proton exchange membrane) water electrolysis;
US11078579B2 / Commissariat à l'énergie atomique et aux énergies alternatives (FR) / Component constituting an HTE electrolyser interconnector or SOFC fuel cell interconnector and associated production processes;
KR101991730B1 / De Nora Permelec Ltd (JP); Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (JP) / Anode for alkaline water electrolysis and method for producing anode for alkaline water electrolysis;
JP6615682B2 / De Nora Permelec Ltd (JP); Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (JP) / Anode for alkaline water electrolysis and method for producing anode for alkaline water electrolysis;
Rating: 20
CN112126946B / CAS DICP Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (CN) / Composite membrane for acid-base water electrolysis and preparation method and application thereof;
CA3093203C / De Nora Permelec Ltd (JP); National University Corporation Yokohama National University (JP); Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (JP) / Electrolysis electrode and method for manufacturing same;
US10619255B2 / De Nora Permelec Ltd (JP); Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (JP) / Anode for alkaline water electrolysis and method for producing anode for alkaline water electrolysis;
CA3018074C / De Nora Permelec Ltd (JP); Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (JP) / Anode for alkaline water electrolysis and method for producing anode for alkaline water electrolysis;
CN108779563B / De Nora Permelec Ltd (JP); Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. (JP) / Anode for alkaline water electrolysis and method for producing anode for alkaline water electrolysis;
US11094953B2 / 3M Innovative Properties Company (US) / Electrode membrane assembly having an oxygen evolution catalyst electrodes, and methods of making and using the same.
In this collection, the largest patent families of those having at least one patent published in the past five years comprise 54, 38, and 26 patent documents and are represented by core documents US11018345B2, US11371153B2, and US11459662B2, respectively (Core document is a base document for which a complete description of the invention is available in generally-accessible patent databases):
Method and electrochemical cell for managing electrochemical reactions / P: US11018345B2 / IPC: H01M4/86, C25B1/13, C25B1/14, C25B1/245, C25B1/26, C25B1/30, C25B9/19, C25B11/031, C25C7/00, H01M4/88, H01M8/04089, H01M8/08, H01M8/083, / Swiegers Gerhard Frederick; Nattestad Andrew; Antiohos Dennis; et al. / Aquahydrex PTY Ltd (AU) / Appl. date: 28.01.2019; Publ. date: 25.05.2021 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US11018345B2 / Technology categories: PEME / Technology elements: Els / Problems: LEMP, HCM, LEHD / Technical solution types: M, C / Claims: 26 / Rating: 16; the second most recent document in this family was published on 28.04.2020 (US10637068B2);
Method for operating a water electrolysis device / P: US11371153B2 / IPC: C25B15/02, C02F1/42, C25B15/08, C25B13/08, C25B1/04, C25B9/19, C25B9/23, C25B9/73 / Höller Stefan / Hoeller Electrolyzer GmbH (DE) / Appl. date: 23.04.2018; Publ. date: 28.06.2022 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US11371153B2 / Technology categories: PEME / Technology elements: SAW / Problems: LEMP, HORR / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 17 / Rating: 16; the most recent documents in this family were published on 06.04.2023 (AU2018257600B2) and 09.02.2023 (AU2017411874B2).
Electrochemical reactor comprising liquid-repellant porous membrane / P: US11459662B2 / IPC: H01M6/32, A61B18/04, A61F7/03, A61F7/12, C25B1/04, C25B1/16, C25B1/34, C25B9/19, C25B9/73, C25B11/031, H01G9/02, H01G9/035, H01G9/048, H01G9/07, H01G9/10, H01G9/145, H01G9/21, H01G11/52, H01M6/04, H01M6/16, H01M6/22, H01M6/34, H01M6/36, H01M6/38, H01M10/0566, H01M10/26, H01M10/36, H01M12/08, H01M50/40, H01M50/60, H01M50/618 / Murahara Masataka / M Hikari & Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd (JP) / Appl. date: 22.07.2019; Publ. date: 04.10.2022 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US11459662B2 / Technology categories: OEL / Technology elements: Els / Problems: LEMP, HCG / Technical solution types: D / Claims: 8 / Rating: 12; the most recent document in this family was published on 21.06.2023 (EP3042717B1).
The following abbreviations are used in the documents above: C - Composition; D - Device; M - Method; OEL - Other electrolysis; PEME - Polymer electrolyte membrane electrolysis; Els - Electrolyser; SAW - System as a whole; HCG - High cost in general; HCM - High cost of materials; HORR - High OPEX / Repair & replacement; LEMP - Low efficiency / Main process.
Below we provide short summaries of documents from the above largest patent families:
Patent US11018345B2 was granted to Aquahydrex PTY Ltd (AU) on 25.05.2021. It discloses a design of an electrochemical cell and a method of operating thereof. The cell comprises a gas diffusion electrode, a liquid electrolyte chamber and a gas region, separated by a non-conductive “…porous gas permeable polymer membrane having a wetting pressure greater than 0.2 bar”, (e.g. expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) membrane), which is substantially impermeable to the electrolyte and has a pore size of 50-500 nm. Wetting pressure of the gas diffusion electrode is the same as that of the porous membrane, which membrane is adhered to this electrode. A porous conductive material is attached to the membrane by a binder material comprising a catalyst. According to the method of the invention, in the electrolyte chamber a pressure is applied at a differential of at least 0.2 bar more than that in the gas region. The suggested pressure differential is maintained by a pressure measurement device and a control device between 0.1 bar and 0.3 bar below the wetting pressure.
Authors mention that the invention addresses such problems as energy efficiency and costs such as those related to equipment production and catalysts.
The patent belongs to a patent family comprising 54 documents published in US, AU, CA, WO, KR, RU, BR, EP, JP, MX, and CN between 2015 and 2021.
By the Editorial Board