Aenert news. Invention analysis
Earlier in our articles we revised some aspects of Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHC) technology by analyzing recently patented inventions in the fields of aromatic LOHC compounds (29.09.2023), heterocyclic LOHC compounds (08.09.2023), and hydrogenation process in LOHC (17.10.2023). Now we are going to address the aspect of dehydrogenation of liquid organic hydrogen carriers. Dehydrogenation is a crucial step in the process of hydrogen storage and transportation. It involves extracting hydrogen molecules from the carrier substance, typically achieved through the use of heat and catalysts, for subsequent use in various applications. For instance, hydrogen produced from LOHC is commonly utilized as a fuel in fuel cells. However, the equipment that utilizes hydrogen often requires specific parameters such as purity, pressure, and temperature of hydrogen, as well as the stability of the dehydrogenation process. Patented technical solutions in the field of liquid organic hydrogen carrier dehydrogenation are aimed at solving these and other problems inherent to the process.
For the purpose of the present analysis, we have collected a set of patent documents considered applicable to dehydrogenation of LOHCs. These are inventions disclosing various aspects of dehydrogenation, such as process parameters, relevant equipment, or its integration into a hydrogen production system.
Below is a list of the top applicants by their patenting share in the field of LOHC dehydrogenation.
Applicants share in the intellectual property market, %. Patents, 2019-2023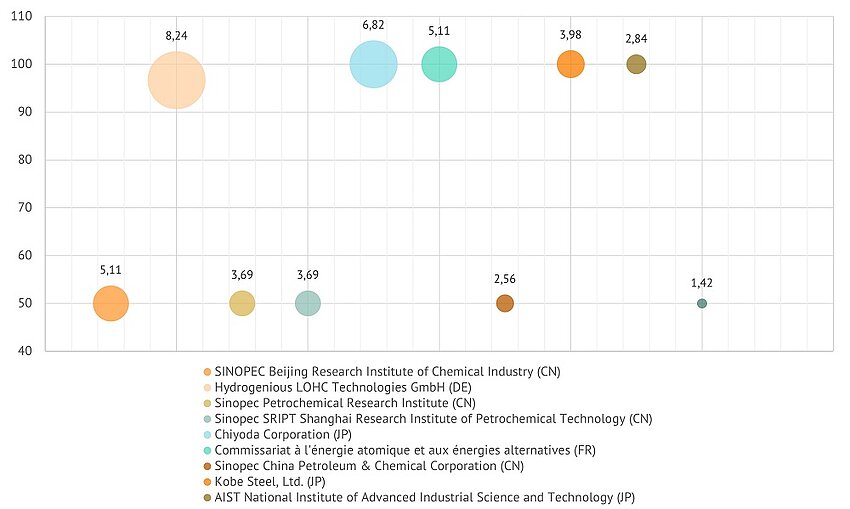
Value: Market involvement ratio*; Y axis: Ownership ratio; Bubble size: Volume ratio.
*(Market involvement ratio = volume ratio multiplied by ownership ratio, where Volume ratio - share of applicant documents in total number of documents, Ownership ratio - applicant's participation share in total number of documents)
In our collection of documents, Sinopec China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (CN) and its affiliated organizations, Hydrogenious LOHC Technologies GmbH (DE), and Chiyoda Corporation (JP) are leading by the number of patents obtained in the past five years.
In the collection of documents under consideration, the largest patent families of those having at least one document published in the past five years comprise 35, 31, and 20 patent documents and are represented by core documents US20210155476A1, AU2020269473A1, and US10450194B2, respectively (Core document is a base document for which a complete description of the invention is available in generally-accessible patent databases):
Batch systems and methods for hydrogen gas extraction from a liquid hydrogen carrier / A: US20210155476A1 / IPC: C01B3/04, B01J16/00, B01J19/00, B01J19/18 / Futerman Roman; Karasenti Erez; Zilberman Alexander; Ginzburg Denis / Electriq-Global Energy Solutions Ltd (IL) / Appl. date: 17.04.2018; Publ. date: 27.05.2021 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US20210155476A1 / Technology categories: OAH / Technology elements: Hdh / Problems: LEHD / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 63 / Rating: 21; the most recent documents in this family were published on 15.09.2022 (US20220293977A1) and 14.06.2022 (US11362348B2);
Organic hydrogen storage raw material dehydrogenation catalyst, carrier of the catalyst, hydrogen storage alloy, and method for providing high-purity hydrogen / A: AU2020269473A1 / IPC: C22C19/03, C01B3/56, C22C14/00, C22C23/06, C22C30/00 / Lin Wei; Yang Xue; Song Haitao; Song Ye; Sun Min; Liu Jun / Sinopec RIPP Research Institute of Petroleum Processing (CN); Sinopec China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (CN) / Appl. date: 06.05.2020; Publ. date: 12.11.2020 / IP Australia / Core document: AU2020269473A1 / Technology categories: OAC, OHC / Technology elements: Hdh, Hct / Problems: EC, HCHD, LEHD / Technical solution types: M, C / Claims: 16 / Rating: 13; the most recent documents in this family were published on 15.11.2022 (CN111892016B) and 21.10.2022 (CN111893360B);
Liquid compounds and method for the use thereof as hydrogen stores / P: US10450194B2 / IPC: C01B3/38, C01B3/26, B01J19/24, C01B3/00, B60K15/03 / Boesmann Andreas; Wasserscheid Peter; Brueckner Nicole; Teichmann Daniel; Dungs Jennifer / Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft (DE) / Appl. date: 27.05.2015; Publ. date: 22.10.2019 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US10450194B2 / Technology categories: OAC / Technology elements: Hdh / Problems: EC, LEHD / Technical solution types: M / Claims: 11 / Rating: 16; the most recent documents in this family were published on 11.01.2022 (BR112015012183B1) and 08.09.2020 (CA2892228C).
The following abbreviations are used in the documents hereinbefore and hereinafter: C - Composition; D - Device; M - Method; OAC - Arene/Aromatic compound; OAH - Alcohol; OHC - Heterocyclic; EC - Ecological problems; HCHD - High cost of hydrogenation or dehydrogenation; LEHD - Low efficiency of hydrogenation or dehydrogenation; Hct - Catalyst; Hdh - Dehydrogenation.
In the pool of inventions disclosing various aspects of dehydrogenation of Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carriers (LOHC), the most popular problems were LEHD - Low efficiency of hydrogenation or dehydrogenation, HLEC - High cost or low efficiency of catalyst, and HCHD - High cost of hydrogenation or dehydrogenation.
The majority of technical solutions provided in the inventions under revision were represented in the form of methods. Devices and compositions were encountered slightly less often in the documents, although in a large number of cases as well.
Just as in the case of Liquid organic hydrogen carrier (LOHC) hydrogenation, here we also paid special attention to patented solutions dedicated to dehydrogenation of toluene, which is considered a promising compound for hydrogen storage and transport.
In the majority of cases, the following IPC indices were assigned to these inventions:
| IPC | Share | IPCs assigned |
|---|---|---|
| C01B3/00 | 8.2% | 79 |
| C01B3/26 | 5.9% | 57 |
| C07C5/367 | 5.1% | 49 |
| C07C15/06 | 3.2% | 31 |
| B01J23/42 | 3.1% | 30 |
| C01B3/22 | 2.9% | 28 |
| B01J35/10 | 2% | 19 |
| B01J23/46 | 1.7% | 16 |
| B01J37/02 | 1.5% | 15 |
| B01J23/89 | 1.4% | 14 |
According to the International Patent Classification, the IPC indices above have the following definitions: C01B3/00 - Hydrogen; Gaseous mixtures containing hydrogen; Separation of hydrogen from mixtures containing it; Purification of hydrogen; C01B3/26 - using catalysts; C07C5/367 - Formation of an aromatic six-membered ring from an existing six-membered ring, e.g. dehydrogenation of ethylcyclohexane to ethylbenzene; C07C15/06 - Toluene; B01J23/42 - Platinum; C01B3/22 - by decomposition of gaseous or liquid organic compounds; B01J35/10 - characterised by their surface properties or porosity; B01J23/46 - Ruthenium, rhodium, osmium or iridium; B01J37/02 - Impregnation, coating or precipitation; B01J23/89 - combined with noble metals.
About 80% of these documents were registered in the CNIPA (CN), JPO (JP), KIPO (KR), USPTO (US), WIPO, and EPO patent offices.
Further, we analyzed the collection of recent patent documents describing various aspects of dehydrogenation and in which toluene is considered the main LOHC carrier compound of the invention. The most popular problems in these documents were low dehydrogenation efficiency (17 documents), degradation of catalyst (7 documents), and complexity of catalyst maintenance (4 documents).
By the Editorial Board