As the continuation of the previous review (Wind Energy 2018/ key indicators), the results of patenting activity of major applicants from patent applications dedicated to horizontal-axis wind turbines in 2018 are briefly evaluated here. 1583 patent applications were collected for the analysis, and are represented by 301 applicants from 29 countries and filed in 28 patent offices around the world. The methodology of searching and processing patent documents is provided on the Advanced Energy Technologies website.
Among the top ten applicants by the number of registered applications are the residents of five countries – Denmark, Germany, the USA, Japan and China. There are top wind turbine producers in the world among them – Vestas Wind Systems A/S, General Electric, Siemens AG, and Senvion S.A. This year, just as the year before, the patenting leaders are Danish Vestas Wind Systems A/S, western German Wobben Properties GmbH and American General Electric. Their aggregate share accounted for nearly 45% of the total number of patent applications.
Top 10 applicants by the number of patent applications filed in 2018
| Status | Country | Name | Average, Rate | Total, 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | DK | Vestas Wind Systems A/S | 13.9 | 301 |
| Company | DE | Wobben Properties GmbH | 11.7 | 247 |
| Company | US | General Electric | 14.4 | 158 |
| Company | DK | LM WP Patent Holding A/S | 10.7 | 62 |
| Company | DE | Siemens AG | 13.8 | 61 |
| Company | DE | Siemens S.A. | 13.4 | 36 |
| Company | JP | Hitachi, Ltd. | 13.8 | 35 |
| Company | DK | Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy A/S | 8.9 | 35 |
| Company | CN | Beijing Goldwind Science & Creation Windpower Equipment Co Ltd | 9.8 | 34 |
| Company | DK | Lm Wind Power International Tech II Aps | 9.9 | 30 |
Source: Advanced Energy Technologies
With some minor exceptions, almost all companies from the top 10 list were the only applicants in their patent applications. Vestas Wind Systems A/S had the highest share in the register of intellectual property for all of the 1583 patent applications collected; it comprised almost 20%.
In addition to national patent offices, all of the aforementioned companies were patenting in foreign offices or WIPO. Wobben Properties GmbH succeeded the most in this regard by registering its applications in 11 patent offices, including the large ones, such as CNIPA (CN), EPO, USPTO (US) и WIPO.
Distribution of patent applications by patent offices around the world among the top 10 applicants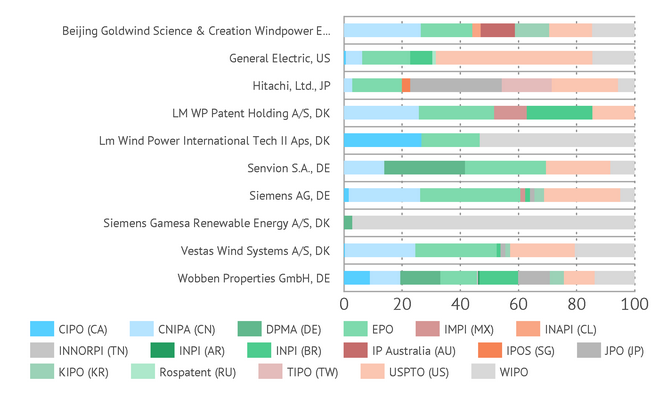
Source: Advanced Energy Technologies
CIPO (CA) - Canadian Intellectual Property Office; CNIPA (CN) - National Intellectual Property Administration; DPMA (DE) - German Patent and Trade Mark Office; EPO - European Patent Organization; IMPI (MX) - Mexican Institute of Industrial Property; INAPI (CL) - National Institute of Industrial Property (Chile); INNORPI (TN) - National Institute for Standardization and Industrial; INPI (AR) - National Institute of Industrial Property (Argentina); INPI (BR) - National Institute of Industrial Property (Brazil); IP Australia (AU) - IP Australia; IPOS (SG) - Intellectual Property Office of Singapore; JPO (JP) - Industrial Property Office (Japan); KIPO (KR) - Korean Intellectual Property Office; Rospatent (RU) - Federal Service for Intellectual Property (Russia); TIPO (TW) - Taiwan Intellectual Property Office; USPTO (US) - United States Patent and Trademark Office; WIPO - World Intellectual Property Organization
Vestas Wind Systems A/S was predominantly patented in CNIPA (CN), EPO, USPTO (US) and WIPO, while General Electric in USPTO (US), EPO and WIPO.
In their patent applications all of the companies from the list of leaders were to some extent concerned with such important wind turbine structural element as Blades and components thereof. Control and safety systems were largely popular as well. Senvion S.A. dedicated a substantial portion of its patent solutions to Aerodynamic casings technology element, while Beijing Goldwind Science & Creation Windpower Equipment Co Ltd. and Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy A/S – to Maintenance, repair and replacement. Often the companies were engaged in the perfection of Structural elements
Technological elements of the top 10 applicants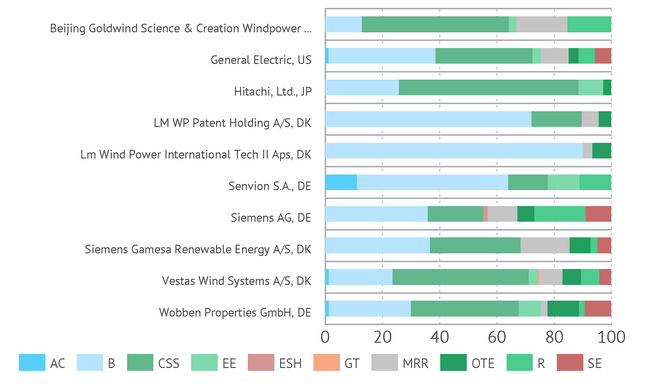
Source: Advanced Energy Technologies
AC - Aerodynamic casings (nacelles, shrouds, etc.); B- Blades and components thereof; CSS - Control and safety systems; EE - Electrical equipment and generators; ESH - Energy storage and hybrid generation systems; GT - Gearbox and transmission; MRR - Maintenance, repair and replacement; OTE - Other technology elements; R - Rotors and components thereof; SE - Structural elements
The proportional correlation of major problems the patent solutions of the companies were aimed at is provided in the chart below.
Distribution of technical problems in the patent applications found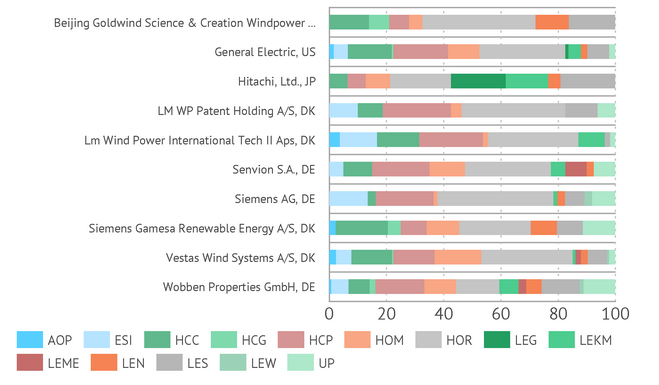
Source: Advanced Energy Technologies
AOP - Administrative and organizational problems; ESI - Environmental and social impact; HCC - High CAPEX / Plant construction; HCG - High costs in general; HCP - High CAPEX / Equipment production; HOM - High OPEX / Operational maintenance; HOR - High OPEX / Repair and replacement; LEG - Low efficiency in general; LEKM - Low kinetic-to-mechanical power conversion efficiency; LEME - Low mechanical-to-electric power conversion efficiency; LEN - Low efficiency caused by secondary natural factors; LES - Low efficiency of secondary equipment; LEW - Low efficiency caused by wind variability; UP - Unclear problem
The inventors were most often focused on the problems High OPEX/Repair and replacement, High CAPEX/Equipment production, High CAPEX/Plant construction and Low efficiency of secondary equipment.
According to our calculations, the highest bibliography rating was gained by, among others, the following patent applications:
- VORTEX GENERATORS FOR WIND TURBINE ROTOR BLADES / A: EP3279467A1 / IPC: B64C23/06, F03D1/06 / Tobin James Robert, Althoff Nicholas Keane, Vossler Alexander William, Johnson Stephen Bertram / General Electric Company / Appl. date: 13.07.2017; Publ. date: 07.02.2018/ VORTEX GENERATORS FOR WIND TURBINE ROTOR BLADES / A: US20180038342A1 / IPC: F03D1/06 / Tobin James Robert, Althoff Nicholas Keane, Vossler Alexander William, Johnson Stephen Bertram / General Electric Company / Appl. date: 05.08.2016; Publ. date: 08.02.2018;
- Tip Extensions for Wind Turbine Rotor Blades and Methods of Installing Same / A: US20180135602A1 / IPC: F03D80/30, F03D1/06 / Tobin James Robert, Hardison Richard, Livingston Jamie T / General Electric Company / Appl. date: 15.11.2016; Publ. date: 17.05.2018;
- Improvements relating to the production of wind turbine components / A: EP3294532A1 / IPC: B29C70/34, B29C70/54, B29L31/08 / HUNTER ROBERT, SMITH JONATHAN / VESTAS WIND SYSTEMS A/S / Appl. date: 11.05.2016; Publ. date: 21.03.2018/ Improvements relating to the production of wind turbine components / A: US20180154593A1 / IPC: B29C70/54, B32B7/08, B32B5/02, B32B27/08, B32B27/38, B29C70/48, F03D1/06, F16B5/00 / HUNTER ROBERT, SMITH JONATHAN / VESTAS WIND SYSTEMS A/S / Appl. date: 11.05.2016; Publ. date: 07.06.2018 / 有关风轮机部件生产的改进 (Improvements relating to the production of wind turbine components) / A: CN107743440A / IPC: B29C70/34, B29C70/54, B29L31/08 / HUNTER ROBERT, SMITH JONATHAN / VESTAS WIND SYSTEMS A/S / Appl. date: 11.05.2016; Publ. date: 27.02.2018.
Obviously, several patent applications having a large number of the WIPO's International Patent Classification sections and focused on the problems of environmental protection should also be considered:
- Imaging array for bird or bat detection and identification / A: US20180163700A1 / IPC: A01K29/00, A01M29/00, A01M29/10, A01M29/16, A01M31/00, E04B1/72, F03D17/00, F03D7/00, F03D7/04, F03D80/00, F03D80/10, G06F3/00, G06K9/00, G06K9/62, H04N5/232, H04N5/247, H04N7/18 / Wenger Eric S, Oliver Andrew G, Babbitt Victor L, Hiester Thomas R / Identiflight Int Llc / Appl. date: 17.11.2017; Publ. date: 14.06.2018;
- Bird or bat detection and identification for wind turbine risk mitigation / A: US20180163699A1 / IPC: A01K29/00, A01M29/00, A01M29/10, A01M29/16, A01M31/00, E04B1/72, F03D17/00, F03D7/00, F03D7/04, F03D80/00, F03D80/10, G06F3/00, G06K9/00, G06K9/62, H04N5/232, H04N5/247, H04N7/18 / Wenger Eric S, Oliver Andrew G, Babbitt Victor L / Identiflight International Llc, Identiflight Llc / Appl. date: 18.10.2017; Publ. date: 14.06.2018.
Some of the single applications that are not members of any patent family and that were prepared by General Electric and Vestas Wind Systems A/S companies are listed below:
- Tip Extensions for Wind Turbine Rotor Blades and Methods of Installing Same / A: US20180135602A1 / IPC: F03D80/30, F03D1/06 / Tobin James Robert, Hardison Richard, Livingston Jamie T / General Electric Company / Appl. date: 15.11.2016; Publ. date: 17.05.2018;
- Segmented Wind Turbine Rotor Blade with Welded Joint / A: US20180298879A1 / IPC: F03D1/06 / Johnson Stephen Bertram, Chen Xu, Walker Alan M / General Electric Company / Appl. date: 12.04.2017; Publ. date: 18.10.2018;
- Connection Joint For A Sectional Wind Turbine Rotor Blade And Associated Methods / A: WO2018121826A1 / IPC: F03D1/06 / BECH Anton / VESTAS WIND SYSTEMS A/S / Appl. date: 19.12.2017; Publ. date: 05.07.2018;
- Joint Assembly for Rotor Blade Segments of a Wind Turbine / A: US20180238300A1 / IPC: F03D1/06, F03D13/10 / Shain Eric Michael, Irizarry-Rosado Xiomara / General Electric Company / Appl. date: 21.02.2017; Publ. date: 23.08.2018.
More detailed information on the methodology as well as on the results of patent researches in the most important fields of contemporary energy industry can be found at Advanced Energy Technologies.
