Aenert news. Invention analysis
Previously, in a series of articles related to solar energy we have revised such aspects of the technology as concentrating photovoltaics (30.04.2023), storage systems (05.06.2022 and 09.01.2023), solar tracking modules (20.06.2022, 22.12.2022, 27.03.2023), and experimental and unconventional solutions (08.04.2023). Now we will take a look at new advancements in the field of solar tracking sensors disclosed in respective patent documents.
For this purpose we have collected more than 1000 inventions published over the past 20 years and analyzed them using the Advanced Energy Technologies methodology.
The patents and patent applications under revision were published in 26 patent offices around the world by 671 applicants from 22 countries.
Solar energy. Tracking sensors. Cumulative number of patents and applications*, relationship of number of applications to total number of documents by year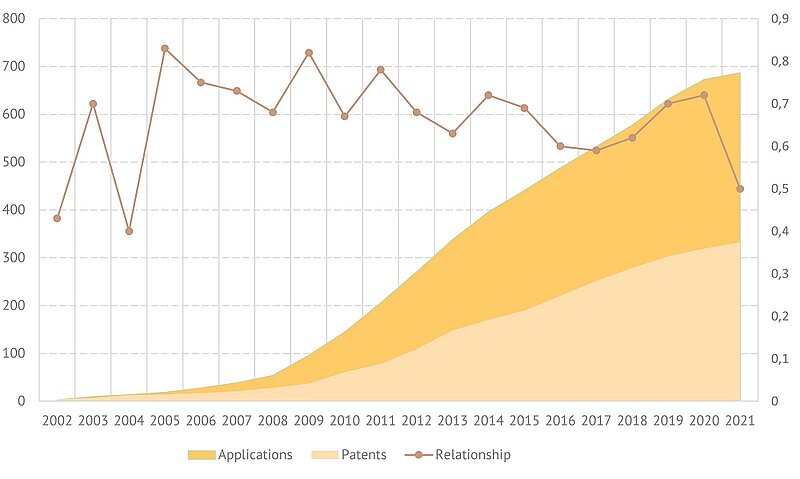
*Areas representing patents and applications are overlapping
In the pool of documents revised for this article, the peak values in the number of published applications were achieved in 2011-2014 and 2019, with a slight decline in the last few years. As for granted patents, the most productive years were 2012-2013 and 2016-2018. Recently, the number of start documents that didn’t belong to any previously formed patent family was well above 70%.
A peak in the number of new applicants appearing in the collection of documents related to the subject under consideration was seen in 2011-2013, after which the values were on moderately high level. In the past few years, the number of new IPC subgroups in the documents was on a high level, achieving the largest value in 2018. The number of new patent offices was substantially stable throughout the period, excluding a spike in 2014. This may indicate a solid interest of the authors in this field of technology with the attempts to integrate solutions from other technical fields into solar tracking sensor technologies. Although, it should be borne in mind that IPC classification has recently undergone substantial changes in the solar energy segment.
During the 20-year period, the largest number of patents were granted by CNIPA (CN) patent office – about 38% of all collected patents related to solar tracking sensors. KIPO (KR) and USPTO (US) followed the leader with almost 28% and around 17%, respectively. JPO (JP), EPO, and TIPO (TW) should also be mentioned as the patenting offices of interest in this field. In terms of recently published patent applications, more than a half of the documents were filed with CNIPA (CN), which was followed by KIPO (KR), USPTO (US), WIPO, and other offices.
Solar energy. Tracking sensors. Breakdown of inventions by patent offices. Patents, 20 years (left); Applications, 5 years (right)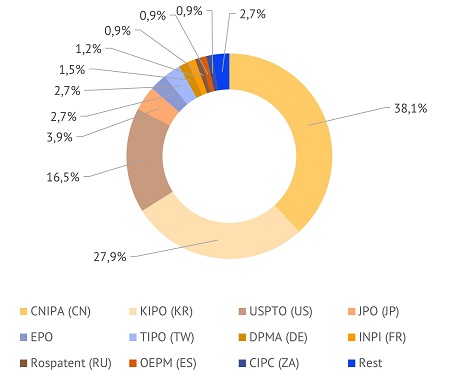
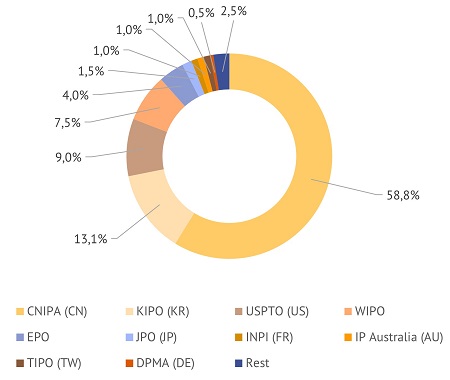
The residents of China are leading in terms of the number of patents granted during the 20-year period with a share of almost 40% of all cases, and recent patent applications – with a share of almost 60%. In both cases they are followed by the residents of South Korea (around 30% and 14%, respectively) and the United States (around 11% and 10%).
Following is a list representing top 10 applicants with the highest Market involvement ratio for patents published in the 20-year period (Market involvement ratio = volume ratio multiplied by ownership ratio, where Volume ratio - share of applicant documents in total number of documents, Ownership ratio - applicant's participation share in total number of documents):
Solar energy. Tracking sensors. Top applicants by Market involvement ratio. Patents
| Status | Country | Name | Volume ratio, % | Ownership ratio, % | Market involvement ratio, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | US | SunPower Corporation | 2.19 | 92.86 | 2.03 |
| Company | ES | Abengoa Solar New Technologies, S.A. | 1.56 | 100 | 1.56 |
| Organization | TW | Atomic Energy Council | 1.56 | 100 | 1.56 |
| Organization | US | Cornell University | 1.56 | 86.67 | 1.35 |
| Organization | CN | Jiangsu University | 1.56 | 100 | 1.56 |
| Company | CH | Elemental Eng Ag | 1.56 | 100 | 1.56 |
| Organization | FR | Commissariat à l'énergie atomique et aux énergies alternatives | 1.25 | 100 | 1.25 |
| Person | US | Moser Mark K | 1.25 | 100 | 1.25 |
| Company | US | CEWA Technologies, Inc. | 0.94 | 100 | 0.94 |
| Organization | DE | Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR) | 0.94 | 100 | 0.94 |
In the collection of patents related to solar tracking sensors the largest number of documents was issued to SunPower Corporation (US), the company was granted 7 patents. It is followed by five applicants, each of which was granted 5 patents: Abengoa Solar New Technologies, S.A. (ES), Atomic Energy Council (TW), Cornell University (US), Elemental Eng Ag (CH), and Jiangsu University (CN). In the collection of recent patent applications, the most active applicants were Elemental Eng Ag (CH) - 7 documents and Jiangsu University (CN) - 6 documents.
Solar energy. Tracking sensors. Top applicants by Market involvement ratio. Applications
| Status | Country | Name | Volume ratio, % | Ownership ratio, % | Market involvement ratio, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | CH | Elemental Eng Ag | 3.52 | 100 | 3.52 |
| Organization | CN | Jiangsu University | 3.02 | 100 | 3.02 |
| Organization | FR | Le Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) | 2.51 | 100 | 2.51 |
| Company | US | Soltec America LlC | 2.51 | 100 | 2.51 |
| Company | CN | Shenyang Xinyuanrui Tech Co., Ltd | 2.51 | 100 | 2.51 |
| Company | DE | Cambras Gmbh | 2.51 | 100 | 2.51 |
| Organization | FR | Commissariat à l'énergie atomique et aux énergies alternatives | 2.01 | 100 | 2.01 |
| Company | CN | Tianjin Fuen New Energy Technology Co., Ltd | 2.01 | 100 | 2.01 |
| Company | DE | Azur Space Solar Power, GmbH | 1.51 | 100 | 1.51 |
| Company | CN | Suzhou Jsolar Incorporated | 1.51 | 100 | 1.51 |
The most commonly encountered problems in the collection of documents under consideration were Low efficiency due to solar movement, High costs of equipment production, and High costs of repair and replacement. Both patents and patent applications generally were disclosed in the form of devices. Methods were encountered in a smaller number of documents, while compositions were not patented at all. The most popular IPC subgroups assigned to the patent documents under revision were: H02S20/32 (specially adapted for solar tracking), G05D3/12 (using feedback), F24J2/38 (employing tracking means), F24S50/20 (for tracking), and H01L31/042 (PV modules or arrays of single PV cells).
The largest patent family in the collection of documents under consideration contains 14 patent documents and is represented by core document US9322437B2 (Core document is a base document for which a complete description of the invention is available in generally-accessible patent databases). It is followed by two patent families with core documents US9658060B2 and WO2017162752A1, each having 12 documents.
Support for solar energy collection / P: US9322437B2 / IPC: H01L31/042, F16C23/02, F16C35/02, F16C23/04, F24J2/54, H01L31/054, H02S20/10 / Agullo Vicent Ripoll / SunPower Corporation / Appl. date: 28/12/2012; Publ. date: 26/04/2016 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US9322437B2 / Technology categories: CPV / Technology elements: SE, TR, Tda, Tsr, Tss / Problems: HCEP, HCPC / Technical solution types: D / Claims: 22 / Rating: 17
Light field image sensor, method and applications / P: US9658060B2 / IPC: G01B11/14, G01N21/64, G01S3/782, H01L27/00, H01L27/144 / Molnar Alyosha, Wang Albert, Gill Patrick / Univ Cornell / Appl. date: 18/08/2014; Publ. date: 23/05/2017 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US9658060B2 / Technology categories: G / Technology elements: TR, Tsr / Problems: HCEP, LEOA / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 11 / Rating: 15
Solar tracking device / A: WO2017162752A1 / IPC: F24S50/20, G01S3/786 / Saeed Osman / Elemental Eng Ag / Appl. date: 22/03/2017; Publ. date: 28/09/2017 / World Intellectual Property Organization / Core document: WO2017162752A1 / Technology categories: G / Technology elements: TR, Tcc, Tda, Tfp, Tsr, Tss / Problems: LESM / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 14 / Rating: 8
The following abbreviations are used in the documents hereinbefore and hereinafter: D - Device; M - Method; CPV - Concentrator photovoltaics; G - CSP or PV in general; HCEP - High costs of equipment production; HCPC - High costs of plant construction; LEEF - Low efficiency due to environmental factors; LEG - Low efficiency in general; LEOA - Low efficiency of optics or absorber; LESM - Low efficiency due to solar movement; CS - Control systems; SE - Structural elements; Tcc - Concentrating collector trackers; Tda - Dual-axis trackers; Tfp - Flat-panel trackers; TR - Trackers; Tsr - Sensors; Tss - Tracking systems.
Solar energy. Tracking sensors. Breakdown of documents by family size. Patents and applications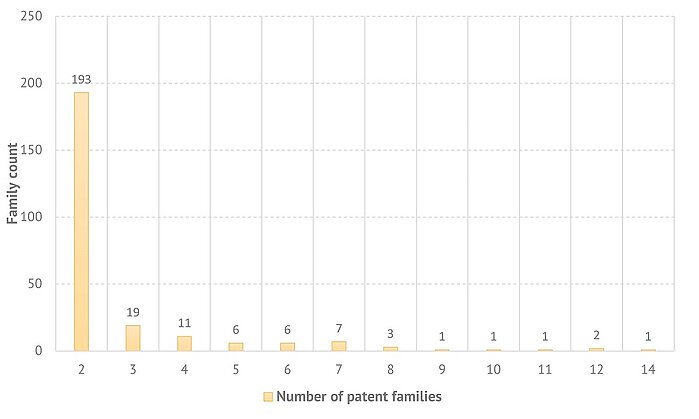
Below we provide several examples of inventions related to tracking sensors with the highest rating calculated using Advanced Energy Technologies methodology:
Solar energy. Tracking sensors. Prominent patent documents by rating:
Suitable Control Method for A System of Photovoltaic Concentration Modules / P: MA35855B1 / IPC: F24J2/38, G01S3/786, G05F1/67 / Ortega Linares Manuel Gil, Rodriguez Rubio Francisco, Guerrero Cano Manuel, Noriega Gil Pablo / ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECHNOLOGIES S.A. / Appl. date: 11/07/2014; Publ. date: 01/12/2014 / Moroccan Industrial and Commercial Property Office / Core document: US20150013751A1 / Technology categories: CPV / Technology elements: CS, TR, Tcc, Tda, Tsr, Tss / Problems: LEEF, LESM / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 16 / Rating: 20
SUITABLE CONTROL METHOD FOR A SYSTEM OF PHOTOVOLTAIC CONCENTRATION MODULES / P: MX344410B / IPC: F24J2/10, F24J2/38, F24J2/40, G01S3/786, G05F1/67, H01L31/02, H02S50/00 / ORTEGA LINARES Manuel Gil, RODRÍGUEZ RUBIO Francisco, GUERRERO CANO Manuel, NORIEGA GIL Pablo / ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECHNOLOGIES S.A / Appl. date: 14/12/2012; Publ. date: 13/12/2016 / Mexican Institute of Industrial Property / Core document: US20150013751A1 / Technology categories: CPV / Technology elements: CS, TR, Tcc, Tda, Tsr, Tss / Problems: LEEF, LESM / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 16 / Rating: 19
Suitable control method for a system of photovoltaic concentration modules / P: US9413290B2 / IPC: G01R31/40, H01L31/042, H01L31/052, F24J2/38, F24J2/40, H01L31/02, G01S3/786, F24J2/10 / Ortega Linares Manuel Gil, Rodriguez Rubio Francisco, Guerrero Cano Manuel, Noriega Gil Pablo / ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECHNOLOGIES S.A / Appl. date: 14/12/2012; Publ. date: 09/08/2016 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US20150013751A1 / Technology categories: CPV / Technology elements: CS, TR, Tcc, Tda, Tsr, Tss / Problems: LEEF, LESM / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 18 / Rating: 19
SUITABLE CONTROL METHOD FOR A SYSTEM OF PHOTOVOLTAIC CONCENTRATION MODULES / P: ZA201404692B / IPC: F24J, G01S, G05F / ORTEGA LINARES MANUEL GIL, RODRIGUEZ RUBIO FRANCISCO, GUERRERO CANO MANUEL, NORIEGA GIL PABLO / ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECHNOLOGIES S.A / Appl. date: 25/06/2014; Publ. date: 31/08/2016 / Companies and Intellectual Property Commission / Core document: US20150013751A1 / Technology categories: CPV / Technology elements: CS, TR, Tcc, Tda, Tsr, Tss / Problems: LEEF, LESM / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 16 / Rating: 18
Suitable Control Method for A System of Photovoltaic Concentration Modules / P: ES2384936B1 / IPC: F24J2/38, G01S3/786, G05F1/67 / Ortega Linares Manuel Gil, Rodriguez Rubio Francisco, Guerrero Cano Manuel, Noriega Gil Pablo / ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECHNOLOGIES S.A. / Appl. date: 15/12/2011; Publ. date: 08/05/2013 / Spanish Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US20150013751A1 / Technology categories: CPV / Technology elements: CS, TR, Tcc, Tda, Tsr, Tss / Problems: LEEF, LESM / Technical solution types: D, M / Claims: 16 / Rating: 18
Thermal tracking for solar systems / P: US8796535B2 / IPC: H01L31/042 / Linderman Ryan J / Sunpower Corporation, Linderman Ryan J / Appl. date: 30/09/2011; Publ. date: 05/08/2014 / United States Patent and Trademark Office / Core document: US20130081668A1 / Technology categories: CPV / Technology elements: TR, Tcc, Tda, Tsr, Tss / Problems: HCEP, LEG, LESM / Technical solution types: D / Claims: 25 / Rating: 18
In the pool of patent documents collected for the present analysis, we have outlined three large groups representing some of the trends in the technical solutions related to solar tracking sensors. The groups include patent documents solving the problems of Low efficiency due to solar movement and High costs of equipment production, and inventions combining solar tracking sensors and tracking mechanisms. Below are several examples of documents from these groups:
- US10690381B2 - improved solar energy collection efficiency is achieved by a solar tracking device comprising a housing with a hole, light wells, primary position sensitive device, auxiliary photodiodes, a lens between the hole and the PSD, and a mask with an aperture between the lens and the hole;
- US11169241B2 - a solar tracking sensor having an optical component comprising a cover plate with a positioning hole and a light transmission hole, a control component, an interface component, and a circuit board that includes a photosensitive detection component and a tilt angle detection component. The invention is aimed to improve tracking accuracy and reduce costs;
- US9857450B2 - improved tracking and lowered costs are achieved by a sensing device comprising a PV sensing section with a hole, a principal optical element (POE) and a CPV receiver. The device comprises a central and a peripheral section that define an aperture for the sunlight to pass to the receiver. A shunt resistor is used for measuring the short circuit current of each cell;
- US20210341180A1 - high accuracy and low costs are achieved by a sensor arrangement comprising an inclination sensor, a camera, and a shadow receiver. The camera is used to sense the shadow of the solar receiver tube;
- US20190253020A1 - a flat panel tracking sensor regulating the position of a supporting unit by analyzing angles of light incident on photodiodes through micro lens made of gradient refractive index material and aimed to lower installation costs.
Low efficiency due to solar movement
Patent US10690381B2 published by Elemental Eng Ag (CH) discloses a solar tracking device comprising a housing with a chamfered central hole and light wells in an upper surface, one primary optical sensor below the hole and auxiliary optical sensors (photodiodes). The light well comprises a rectangular aperture on top, one light-reflective sidewall facing towards or away the central hole, and a bottom surface with the respective auxiliary sensor. The primary optical sensor is an isotropic position sensitive device (PSD) comprising a 2D array of discrete sensors. A lens is disposed between the central hole and the PSD, and a mask with an aperture is placed between the lens and the central hole. The method of the invention comprises "…detecting at least one of: light intensity at the auxiliary sensors; and a position of incident light on the primary sensor; and actuating the at least one drive mechanism in response to the detected light with the objective of balancing the light intensity at the auxiliary sensors and centering the incident light on the primary sensor".
The authors of the invention mention low energy collection efficiency as one of the prior-art drawbacks. The sensor can be used in photovoltaic panels and is applicable to dual axis solar tracking devices.
The patent belongs to a family comprising 14 patent documents published in WO, TW, KR, CN, EP, US, JP, and ZA between 2016 and 2022.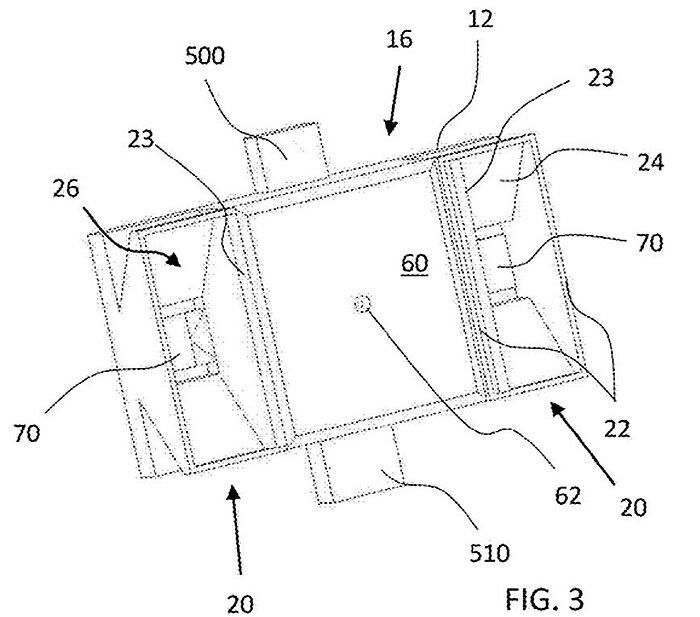
Image from US10690381B2
12 - housing; 16 - central portion; 20 - lateral portions; 22,23,24 - sidewalls; 26 - rectangular opening; 60 - mask plate; 62 - aperture; 70 - optical sensor; 500 - magnetometer module; 510 - inclinometer module.
Patent US11169241B2 published on 09.11.201 by Suzhou Jsolar Incorporated (CN) describes a sensor with a protective housing and an optical component comprising a cover plate with a positioning hole and a light transmission hole with two openings, a control component, an interface component, and a circuit board. The circuit board includes a photosensitive detection component (facing a radiation source) and a tilt angle detection component (away from a radiation source). The sensor can further include a communication component. The protective housing comprises tempered glass and includes an outlet (four core outdoor shielded cable), a waterproof vent, and a circuit board positioning interface. The patent further describes an embodiment of the sensor comprising two vertically-arranged optical components made of a black weather resistant material, and five photosensitive elements (one for sensing radiation intensity, and two vertically-arranged groups of two photosensitive elements). The claims of the invention further disclose a solar tracking system comprising the patented sensor, and a method of its operation.
The authors of the invention claim that the sensor can ensure a high-precision tracking control, and mention cost issues as the drawbacks of the prior-art solutions. The invention can be used in solar photovoltaic panels.
The patent belongs to a family comprising 7 documents published in 2017-2021 in the CN, WO, and US patent offices.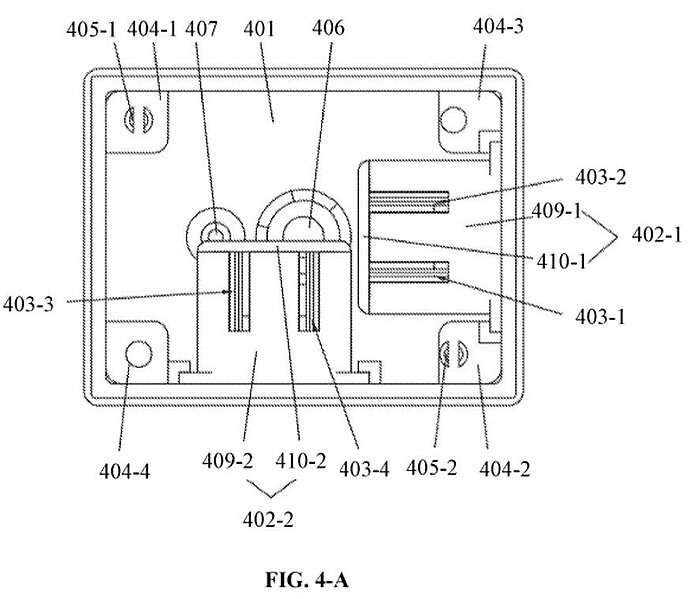
Image from: US11169241B2
401 - protective housing; 402-1,402-2 - optical component; 403-1,403-2,403-3,403-4 - optical channels; 404-1,404-2,404-3,404-4 - bumps; 405-1,405-2 - plug connectors; 406 - outlet; 407 - waterproof vent; 409-1,409-2 - body; 410-1,410-2 - cover plate.
High costs of equipment production
Patent US9857450B2 by Vilella Ricard Pardell (ES) describes a sensing device for the alignment of a CPV device with respect to the sun. The sensing device consists of at least one photovoltaic sensing section having a hole and placed between a principal optical element (POE) and a CPV receiver. The hole allows substantially all sunlight to pass through and impinge the CPV receiver when perfectly aligned. The photovoltaic sensing section comprises a plurality of cells and each having a truncated corner and the hole in the center when arranged together. The sensing device comprises a central and a peripheral section that define a sensing device aperture, which allows the sunlight to pass through to the CPV receiver. The central and peripheral cells are connected to a shunt resistor for measuring the short circuit current of each cell. The device also includes four light blocking walls normal to the POE focal and aperture planes. The claims of the invention further provide other details of the sensor, a tracking system incorporating the sensor, and a method of controlling the tracking process employing the sensor.
Among the advantages of the invention, the authors mention increased tracking reliability and reduced costs, including manufacturing costs.
The patent is a part of a patent family comprising 4 documents published in 2013-2018 in WO, EP, and US.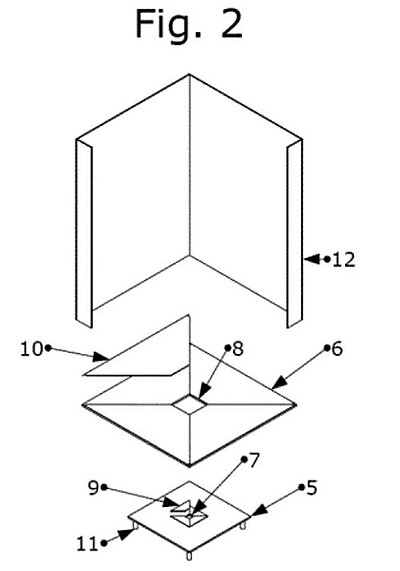
Image from: US9857450B2
5 - Central section; 6 - peripheral section; 7 - square hole; 9,10 - photovoltaic cells; 11 - four standoff inserts; 12 - light blocking walls.
Patent application US20210341180A1 by Cambras Gmbh (DE) discloses a tracking sensor arrangement for a solar collector assembly comprising a housing with an inclination sensor and a camera. A shadow receiver extends from the housing and is positioned to receive a shadow of the solar system receiver tube, and the camera is used to sense the shadow on the receiver. The sensor arrangement can be mounted in an apex area of a parabolic trough mirror to receive the shadow of the receiver tube. At least one or two side shields extend along the whole length and/or height of the housing, spaced from the housing by a heat-resistant material with low thermal conductivity. The camera is positioned at an angle to the shadow receiver, less than 90 degrees, or about 45 degrees. The sensor housing comprises a thermal exchanger and a copper plate to cool or heat the camera and the inclination sensor. The housing also includes a main carrier onto which the camera and the inclination sensor are mounted. The claims of the invention also describe the method of operation of such sensor arrangement.
The authors claim that the sensor arrangement of the invention can be manufactured at low cost and provide high accuracy.
The application belongs to a patent family consisting of 6 documents published in the WO, AU, US, EP, CN, and ZA patent offices between 2020 and 2023.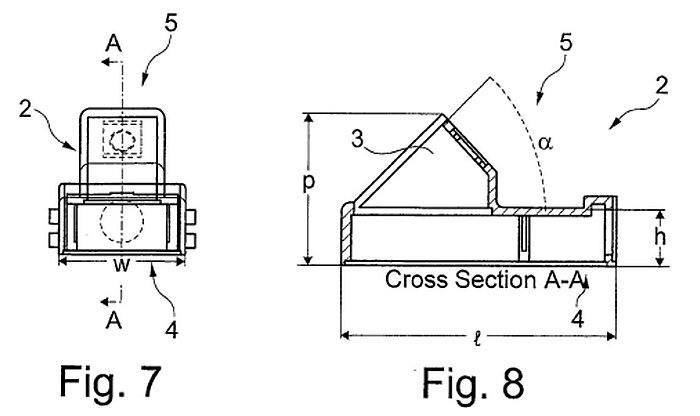
Image from: US20210341180A1
2 - housing; 3 - protruding portion; 4 - back side; 5 - front side.
Tracking mechanisms
Patent application US20190253020A1 published by Shanghai Integrated Circuit Research & Development Center (CN) discloses an image sensor for solar tracking. The image sensor has incident angle sensitivity, and includes multiple pixels (photodiodes) and a micro lens made of gradient refractive index material which only refracts light with a certain incident angle to make such light vertically incident upon the photodiode. The light is photoelectrically transformed by the photodiode and an electric signal is produced. Different micro lenses have different gradient refractive index materials to provide different refracted incident light angles corresponding to the various angles of the sunlight. The sensor further comprises an identification unit to identify the angle of sunlight based on electric signal strength, and a control unit to regulate the position of the supporting unit according to the incident angle. The claims of the invention further provide additional details of the proposed sensor, its operation principles, and tracking mechanism used in the tracking process. The sensor of the invention is applicable to solar panels.
According to the authors of the patent application, reduction of installation costs is among the objects of the invention.
The document is a single application published in the USPTO patent office in 2019.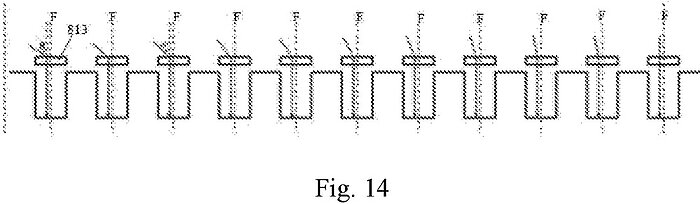
Image from: US20190253020A1
During the analysis of these and other documents in the collection, it was revealed that in a large number of inventions, the authors tend to combine tracker sensors with heliostat angle adjustment systems and supporting structures. In the collection of documents, approximately the same number of inventions relate to concentrating and non-concentrating systems. At the same time, a significantly larger number of dual-axis trackers was encountered, compared to the single-axis trackers.
More detailed information about inventions in the field of solar energy, and patent research methodology can be found on aenert.com, in SOLAR ENERGY. Solar Trackers. Extended patent report. June 2022, and CONCENTRATED SOLAR POWER. Energy Storage. Patent Database. May 2022.
By the Editorial Board
