Aenert. Research Laboratory news
Modern energy systems are becoming ever more complex and interdependent. In order to prepare them for the full transition to green energy production and enable operation at full capacity, you have to have a precise understanding of how the interdependencies work, model and analyse them carefully so that your can monitor and control them properly.
Nowadays if, for example, someone wants to install a photovoltaic system, a heat pump or a charging station for electric cars they need to contact their energy network operator first to find out whether establishing a connection to the public network is possible. At present, this process is time-consuming and also difficult to coordinate because it is carried out manually. However, as the energy market is currently experiencing great changes due to an increasing number of renewable power stations or charging stations for electric vehicles being connected to the grid, the need for more efficient and comprehensive digital systems is becoming an ever important task for energy operators.
Now (2022), scientist at Fraunhofer Institute for Energy Economics and Energy System Technology IEE have designed a system called retoflow, which presents network operators with a software solution to automating the connection checking process. The system creates a digital twin of the fully digitalised energy network. The web-based platform is designed in a manner that it retrieves the relevant network data, analyses the impact of the system at the different network levels, tests its technical feasibility and checks whether a network expansion would be needed.
The system is also suitable for the long-term planning of power grids and pipeline networks as it employs a metaheuristic outlining future network configurations and planning and making recommendations concerning whether to build new or dismantle old lines. The overview mode makes it possible to view all supply lines and affords a detailed picture of the network model. The system can also project overloaded lines and future cable routes. Retoflow calculates the routing, line utilisation, voltage differences and other technical parameters in real time and also estimates the costs involved. The idea behind the software was generated using the open-source programs system modelling tolls pandapipes (pandapipes.org) and pandapower (pandapower.org).
Retoflow usually operates in the cloud. However, it can also be hosted on site by the network operator. The software is currently designed to model power grids. The team of scientists intend to expand it so that it can also be used to plan gas and heating networks.
Scientists have long tried to optimise the production as well as the distribution of energy. In 2021, a model was designed to include investments in demand flexibility into traditional transmission expansion problems. To this end, a dynamic power flow model was developed. The model was calculated applying a value function approximation in form of a neural network on the operational problem, which yielded a result for the non-convex investment problem. Additionally, robust sets were applied and linearised to tackle uncertainty and decrease computational complexity. Similarly, Karush Kuhn Tucker conditions, first derivative tests for a solution in nonlinear programming to be optimal, were employed to transform a tri-level into a bi-level problem. Case studies for systems of varying complexity showed the convergence of the algorithm as well as that the resources which could be used as a cost-effective substitute for transmission lines in grid expansion were flexible.
Image: Network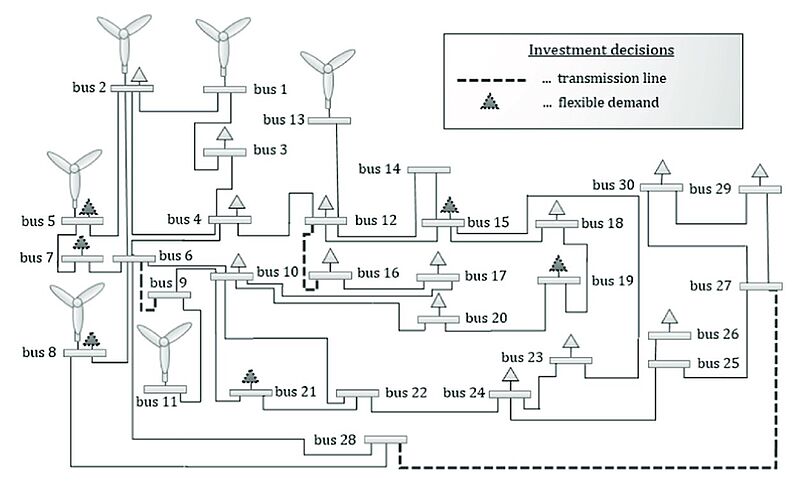
Source: Markus Löschenbrand/ A transmission expansion model for dynamic operation of flexible demand/ International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 124:106252, January 2021/ DOI:10.1016/j.ijepes.2020.106252/ Open Source Open Access This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
In 2022, the sufficiency of an aggregated flexibility model for planning tools was analysed by comparing it against a detailed flexibility model. Two different constraint formulations, based on recovery period as well as temporal proximity, were analysed to account for post activation dynamics of flexibility resources. The results showed that the recovery period-based formulation led to great demand reduction. The proximity constraint formulation on the other hand was responsible for realistic activation of flexibility resources. This was an improvement over the base formulation without constraints for post activation dynamics.
Image: Temporal interdependencies as represented by proximity constraints for load shifting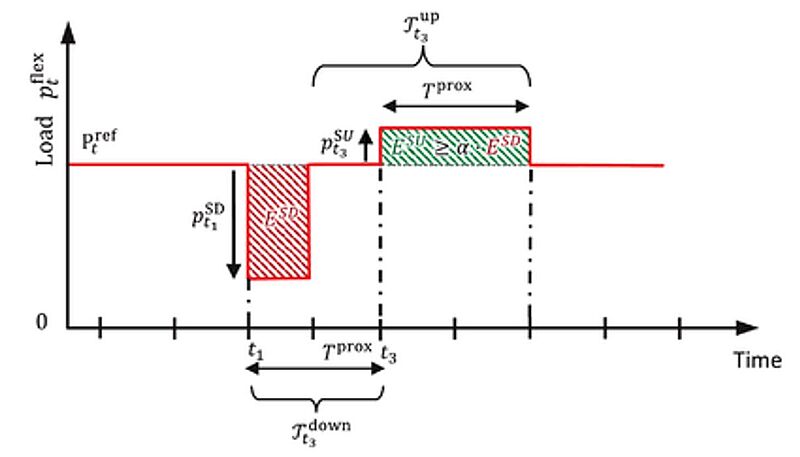
Source: Espen Flo Bødal, Venkatachalam Lakshmanan, Iver Bakken Sperstad, Merkebu Zenebe Degefa/ Demand flexibility modelling for long term optimal distribution grid planning/ IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution 16(24):n/a-n/a, November 2022/ DOI:10.1049/gtd2.12651/ Open Source Open Access This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
The advantages of retoflow are at hand: As the process of energy systems integration continues, energy, heating and gas networks will be increasingly combined and merged. However, network operators and public utilities are still managing the various technologies facilitating the energy transition separately. Retoflow can support the development of merged systems by providing a comprehensive planning tool for the different sectors.
Over the last couple of years there has been a sharp increase in the number of requests to utilities concerning solar power installations or vehicle charging stations and their number will surely become even greater in the years to come. The retoflow system once implemented at large scale will have great impact on the efficiency of the power grid. A number of pilot customers have already successfully tested the program, among them the public utility Stadtwerke Fürstenfeldbruck, as well as the network operators Netze BW and BS Netz.
By the Editorial Board