Aenert news. Energy Companies
Solar photovoltaics continue to show consistent and promising results. According to Irena, at the end of 2022, the total installed capacity worldwide exceeds 1,000 GW, significantly outpacing wind power. The largest photovoltaic capacity is concentrated in China – 37.5% or 392.5 GW, Europe – 21.5% or 225.5 GW and the US – 10.7% or 111.5 GW. Together, these three regions account for about 70% of all installed global capacity. With India (62.8 GW) and Japan (78.8 GW), the share of these five regions increases to 83%.
In the last three years, the growth rate of new capacity worldwide has been maintained at an average annual rate of 20%, while the total capacity worldwide has increased by about 7.5 times in ten years. In 2022, installed capacity grew by 28% in China, 20% in Europe, and 8.7% in the United States. At the same time in China and Europe these figures were significantly higher than in pre-pandemic 2019 (by 11% and 3%, respectively), and only in the U.S. there was a decrease from 19.1% to 8.7%.
The recent 16th International Photovoltaic Power Generation and Smart Energy Conference and Exhibition in Shanghai demonstrated the enormous interest of both manufacturers and consumers in solar energy. The event was attended by several hundred thousand visitors and more than 2,800 exhibitors.
The above mentioned figures generally indicate the large-scale expansion of photovoltaics in the electric power market. Nevertheless, the volume of PV power generation still leaves much to be desired. Thus, in the last quarter of 2022, the share of photovoltaics in the total amount of electricity generation was 4% in Europe, 2.9% in the U.S. and 2.5% in China, being noticeably less than the share of wind power. However, it should be noted that these figures are higher than in the same quarter of the previous year.
Below is a summary of the financial and operating results of PV industry leaders from around the world for the first quarter of 2023 (2023Q1).
Longi
Longi is one of China's largest public companies and one of the world's largest manufacturers of mono- and polycrystalline silicon products, photovoltaic cells and solar modules. In addition, Longi produces equipment for hydrogen production through electrolysis as well as batteries. The company operates in 150 countries in all major regions of the world, but its main market is China.
Longi. Revenue, net income and share price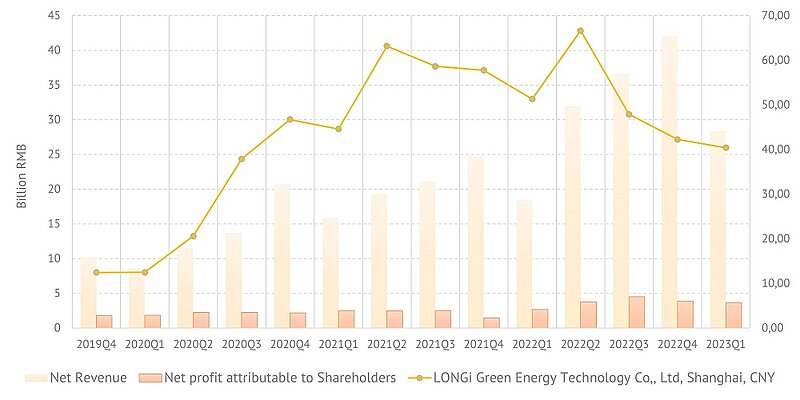
Keeping up with market trends related to changes in silicon demand and prices, in 2022 the company carried out expansion of production capacities with high-efficiency technologies, including smart production. At the same time, shipments of silicon wafers in 2022 increased by 27% over the previous year, solar cells by 25% and solar modules by 25%. This is due to the longstanding practice of significant investment in research and development, which amounted to more than 28 billion yuan over the past 10 years. The company has over 4,000 employees in the research sector. Longi also holds 2,132 patents.
This strong operating performance is also reflected in the company's financial results. Longi has a multi-year steady growth in operating revenue, as well as a constant and growing net profit. In 2023Q1 the company's Total Revenue was 28.3 billion yuan (52% more than a year earlier) and Net Profit attributable to shareholders rose 37% to 3.64 billion yuan. Wafer shipments in the quarter increased by 24%, Cell & Module shipments by 12.6%. Indicator of the company's achievements is the large number of awards and nominations, such as the high PVMI indices received from the U.S. Renewable Energy Testing Center. The company is also well positioned on the stock market.
First Solar Inc.
The company was founded in 1999 and is currently the leading American company in the field of solar energy. Unlike most other companies that use crystalline silicon in PV designs, First Solar specializes in the production of thin film PV modules with a layer of Cadmium Telluride (CadTel) semiconductor. The company's main production facilities are located in the United States (Ohio), and the company is not dependent on vulnerable logistics supplies from China.
First Solar's thin film photovoltaic technology features low semiconductor material usage, low power consumption, and a lower environmental impact than traditional technologies. First Solar's thin film modules feature a superior degradation rate, temperature coefficient, spectral and shading response. In addition, the company reported a World record CdTe research cell conversion efficiency of 22.3%.
First Solar. Revenue, net income and share price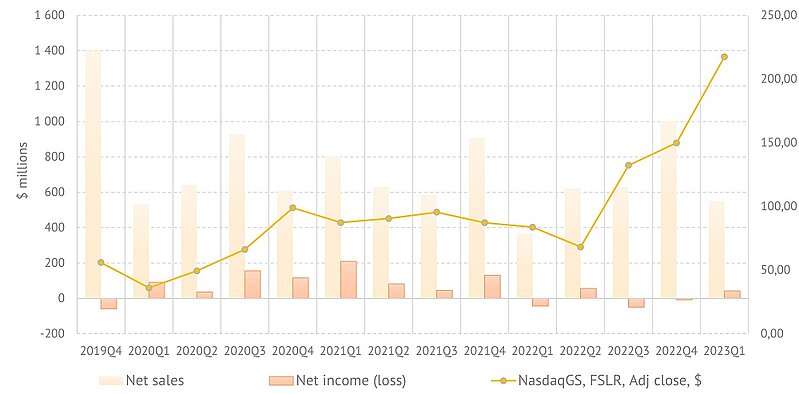
2022 was not the most successful year for First Solar from a financial point of view, but the company launched the most advanced modules of the 7 Series, and its total sales exceeded $2.6 billion. The company's annual Net Loss was $44 million. In the first quarter of this year the company's Net Sales were $548.3 million (1939 MW) which is 54% higher than the same quarter a year ago, but $454 million less than in 2022Q4. The company's press release says the following: "...The decrease was primarily driven by a decrease in the volume of modules sold to third parties". However, the company turned a respectable net income of $42.5 mln.
According to the company's near-term plans, a global production network with an annual capacity of 20 GW, including India, Malaysia and Vietnam in addition to the U.S., will be created by 2025.
The prospects for the development of thin film PV modules with CdTe layers are often looked at with considerable skepticism, despite the good progress in cell conversion efficiency. This is due to the fact that tellurium is a fairly rare metal, and its exact reserves are difficult to estimate. According to USGS calculations (based on identified copper deposits and average tellurium content), the largest reserves of this metal in the world are in Russia, the U.S. and China, with its imports to the United States over the past five years falling by more than four times and its price has also decreasing markedly. In addition, over 90% of tellurium is recovered from anode slimes collected from electrolytic copper refining. Moreover, thanks to First Solar, the recovery of tellurium from the company's own recycled tellurium from CdTe solar cells has begun. Thus, the raw material supply of tellurium to First Solar's plants in the United States looks quite convincing. As for other countries, the company obviously has reliable data to predict with confidence the prospects of expanding production outside the U.S.
Jinko Solar Holding Co.Ltd.
Jinko Solar is one of the largest companies in the solar power industry. By the end of the first quarter of 2023, the total volume of solar PV modules delivered by the company to various markets reached 150 GW. The company has a customer base of over 3,000 in 160 countries. Jinko Solar is a vertically integrated company encompassing all elements of the production chain from silicon wafers to solar modules. Its 14 plants are located in China, the United States, Malaysia and Vietnam. More than 1,000 employees work in the company's research units. The company is headquartered in Shanghai, China.
Jinko Solar is known for its original innovative solutions, including:
- Half Cell module technology, which reduces shading losses and lowers the panel temperature, thereby increasing power generation efficiency;
- Bifacial Module with Transparent Backsheet technology, providing up to 20% power gain;
- Tiling Ribbon, providing elimination of the gap between the cells and reducing the occurrence of micro-cracks.
Jinko Solar. Revenue, net income and share price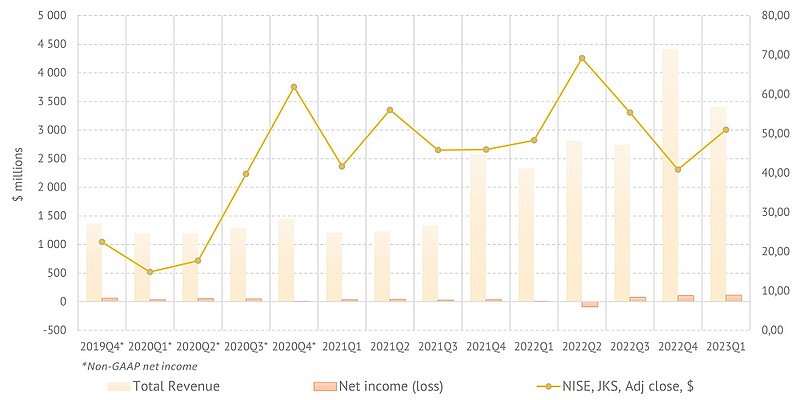
Jinko Solar has been demonstrating solid financial and production results over the past years. In the first quarter of this year, the company shipped product estimated at $3.4 billion (14.5 GW), or 46% more than a year earlier. However, the real yield for the company was 2022Q4, when it shipped 16615 products estimated at $4.35 billion. The last three quarters were profitable for the company, especially the last one, when GAAP net income was $115 million. However, it is worth noting the relatively low net margin, which was 3.6% in the last quarter, but usually has lower values.
Canadian Solar
Canadian Solar, founded in 2001, is one of the world's largest solar module and energy storage battery companies. By the end of 2022, Canadian Solar had installed approximately 88 GW of photovoltaic modules in more than 20 countries. The company is headquartered in Ontario, Canada. The company employs more than 13,000 people and has production facilities not only in Canada, but also in China, Brazil, Indonesia and Vietnam. In recent years, the company has consistently demonstrated not only a break-even performance, but also high profitability.
In the first quarter of this year, the company began mass production of its flagship N-type TOPCon Bifacial Module with a twelve-year warranty on materials and workmanship and a thirty-year warranty on linear power output. This module currently has Front side power up to 695W, with plans to increase it to 700W. The company uses mono-crystalline and poly-crystalline silicon as the active element in its solar modules. In addition to module production, the company is involved in project development, system design, engineering and financing.
In 2023Q1, Canadian Solar saw a 66% year-over-year increase in shipments to 6.1 GW with revenues of $1.7 bln. These figures are markedly lower than in 2022Q4, which the company attributes to an expected decrease in the average selling price of certain module brands, lower solar module shipments due to seasonality, and lower project sales. At the same time, net income attributable to Canadian Solar in 2023Q1 amounted to $84 million, which is the best result in the last two years.
Canadian Solar. Revenue, net income and share price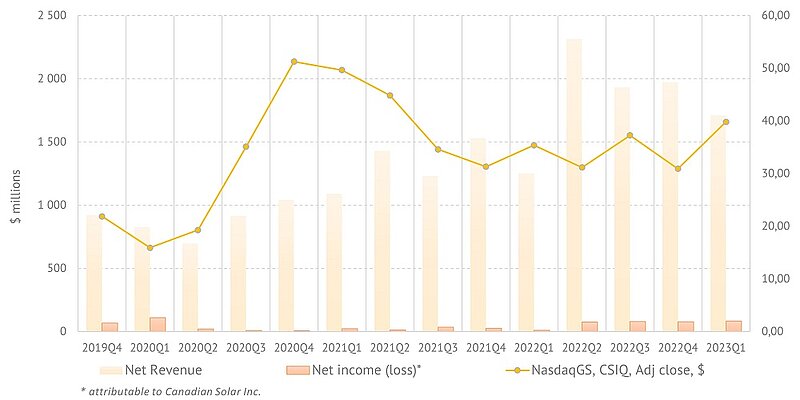
The four publicly traded solar companies considered here are almost invariably among the top 10 in terms of both output and capitalization. In addition, these companies have installed more than 40% of the total volume of PV modules around the world, and their production facilities are concentrated in different regions of the world. This suggests that the activities of these companies largely reflect the state of the entire industry. Judging by the data presented, solar PV has been on the rise in recent years, despite the challenging periods of the coronavirus pandemic in 2020 and political tensions in 2022. These results promise an optimistic outlook for the future.
However, the flip side of this process could be uncontrolled expansion of production, lower product prices and a wave of bankruptcies. Bloomberg points this out for example, in its article Top Solar Firm Warns Excess Capacity Risks Wave of Failures. Nevertheless, it is obvious that these are inevitable aspects of free market regulation itself, the result of which is usually the consolidation of production of the most stable players and the gradual recovery of the initial conditions. More painful for the further development of this energy sector may be its direct dependence on the general trend of the world economy, the direction of which is still uncertain, balancing between signs of both growth and slowdown, or recession from region to region and from quarter to quarter. In this regard, 2023 is likely to be a defining year for the global economy as a whole and for individual energy sectors, including solar.
By the Editorial Board
