In recent years cellulosic ethanol production rates have tended to demonstrate moderate growth. This technology makes it possible to avoid using food crops for the production of energy carrier that can be used as an additive for conventional types of fuel. During the last decade ethanol production technologies have become widely used in the USA, Brazil and the European Union, while total volumes of ethanol produced in 2015 exceeded 25 billion gallons.
The development of cellulosic ethanol production technologies requires sufficient number of research organizations and industrial enterprises that would introduce and implement innovative solutions.
The present report contains information on top-10 patent applicants who published patent applications in this field in 2015. For these purposes we analysed 340 applications that were filed in 28 patent offices and summarised the participation data for 98 applicants from 23 countries.
The table below provides the top-10 patent applicants
| Status | Country | Name | Average, Rate | Total, 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | US | Xyleco Inc. | 9.5 | 30 |
| Company | US | API Intellectual Property Holdings LLC | 6.8 | 20 |
| Company | NL | Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. | 9.1 | 17 |
| Organization | FR | IFP (École Nationale Supérieure du Pétrole et des Moteurs) | 7.2 | 12 |
| Organization | FR | Le Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) | 7.2 | 12 |
| Company | US | BP Corporation North America, Inc. | 6.6 | 10 |
| Company | US | EI du Pont de Nemours and Company | 5.5 | 8 |
| Company | FI | Neste Oil | 7.8 | 8 |
| Company | DK | Novozymes A/S | 6.6 | 8 |
| Company | US | Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC | 6 | 8 |
Comparison to a similar list for the previous year shows that 6 out of 10 applicants have changed.
Companies that appear in the list of active patent applicants for the second year in a row are: Xyleco Inc. and API Intellectual Property Holdings LLC (in 2014 they were both holding leading positions as well); BP Corporation North America, Inc. and Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC.
Such companies as Xyleco Inc., API Intellectual Property Holdings LLC, Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V., Neste Oil and Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC are also present among the leaders in terms of publishing patent applications outside their respective country or residence.
In the selection of documents examined Xyleco Inc. covers the greatest number of patent offices – patent applications were published in the patent offices of the USA, Japan, Australia, Eurasian Patent Organization, Israel, Brazil, Singapore and New Zealand. It is followed by Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC, which published patent applications in the offices of the European Patent Organization, New Zealand, Japan, South Korea, China, the USA and the World Intellectual Property Organization. The other companies from this list cover from 3 to 5 patent offices.
The Average Rate column in the table above displays aggregate bibliographical patent document rating, which evaluates documents by the sum of their bibliographical parameters; these include the number of registered claims, document type, problems declared in the description, technological belonging, and many others.
Among all the examined patent applications published by the applicants from the top-10 list the most frequently met IPC class is C12P, which in short represents fermentation processes to synthesise or to separate a desired chemical compound. The second most popular IPC class is C12N, which represents microorganisms or enzymes; compositions thereof; propagating, preserving, or maintaining microorganisms; mutation or genetic engineering; culture media.
In the majority of cases the companies were attempting to use their inventions to solve the problem of poor efficiency in the main technological process. Only three companies from the top-10 list have prioritized other problems: Neste Oil (high costs and low efficiency of processes caused by the variety of feedstock); Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC (high costs); and Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij B.V. (high costs and environmental issues). High costs is the second most popular problem concerned in the documents of the top-10 applicants in the present patent document collection.
The top-10 applicants generally put forward solutions in the form of technical methods and procedures in the field of cellulosic ethanol production. A considerable number of documents are also dedicated to biological or chemical compositions, and quite a small number of documents disclose structural design of devices. Exceptions here are IFP and CNRS organizations, which prioritized biological or chemical compositions, and Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC, which paid major attention to structural design of devices.
The chart below shows the structure of technological interests for top-10 applicants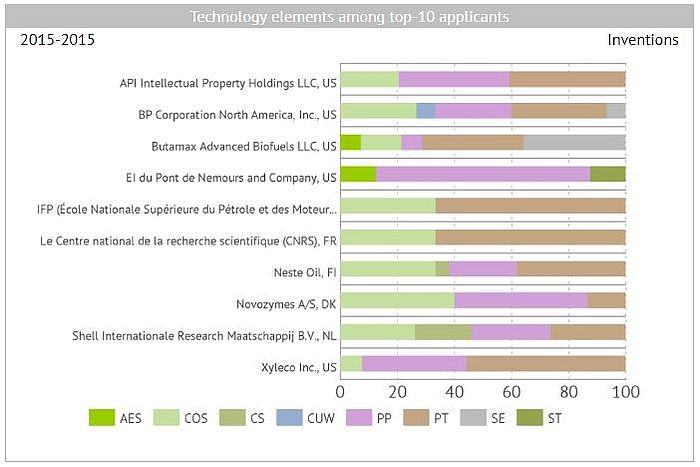
PT - Pre-treatment of feedstock; FS - Feeding systems; PP - Primary processing; COS - Chemistry and other substances; CS - Capture and separation; SE - Secondary equipment; CD - Methods of control and diagnostics; CUW - Capture, utilization of solid, liquid and gaseous wastes; AES - Additional equipment, substances; FT - Finishing treatment; ST - Storage & transportation; PTG - Processing technologies in general
The chart above indicates that in the majority of cases the applicants focused on the technologies of preliminary processing and preparation of feedstock, as well as on the technologies, equipment and compositions used in the main reactions of biomass processing.
More detailed information on the methodology, as well as on the results of patent researches in the most important fields of contemporary energy industry can be found on www.aenert.com
